Generative AI (GenAI) represents a potentially transformational opportunity for information companies to enhance the value they create for customers and to embed more deeply in workflows then ever before.
Information companies with unique, high-quality data and an intimate understanding of their customers’ needs and use cases are best placed to take advantage. They have the curated data and understanding required to train well-tailored and reliable GenAI models, and the industry trust and credibility to promote adoption.
How are information companies innovating with Generative AI?
Two broad focus areas are emerging:
- Customer value proposition enhancement
- Productivity in data collection
1. Customer Value Proposition Enhancement
The last few months has seen a flurry of announcements from major information companies unveiling their first customer-facing GenAI innovations. Whilst the major focus has been on the development of AI assistants in this first wave of innovation, there is potential for significant enhancements to user value propositions.
Three core functionalities of note are:
Conversational search and summarization:
- Generative AI enables users to engage in conversations with chatbots in order to find quick answers to specific questions
- For example, FactSet AI enables customers to ask questions like “Which banks have the most exposure to CRE loans?”, and AlphaSense Assistant answers questions such as “What are the key takeaways from the Google Q2-23 Earnings Call?”
Output drafting:
- GenAI can create personalised drafts of emails, letters or documents on behalf of users. For example, Lexis+AI helps lawyers to write emails to clients and to draft legal arguments.
Integration of clients’ internal data
- Some providers have introduced the ability for customers to upload internal data onto their platforms, and to deploy their specialised GenAI models against the integrated/combined universe of data. This is particularly valuable for clients with data embedded within multiple document formats, such as internal presentations, pitch packs, emails and meeting notes.
- For example, AlphaSense’s “Enterprise Intelligence” tool enables customers to use AlphaSense’s proprietary GenAI tool to search and summarise internal data.
- The early examples of innovation with integration of clients’ internal data reflects an opportunity for information companies to become much larger and more critical central data / knowledge management platforms which integrate clients’ internal and external data sources across multiple platforms.
For examples of recent launches see Lexis+AI, AlphaSense Assistant, FactSet AI and BloombergGPT.
2. Productivity gains in data collection
Collecting, cleaning, structuring and analysing data are fundamental processes for information businesses and typically comprise a substantial proportion of their cost base. These activities involve repeatable tasks which can be replaced or augmented by GenAI, and have been an initial focus area for information service companies.
Example use cases Plural has seen deployed are:
- Information extraction – extracting data from multimedia formats, particularly video, audio text and images.
- Data cleansing – detecting outliers to identify potential errors, and in some cases, imputing missing values.
- Content generation – generating first drafts of articles that are later updated by researchers and analysts.
How might Generative AI transform the sector?
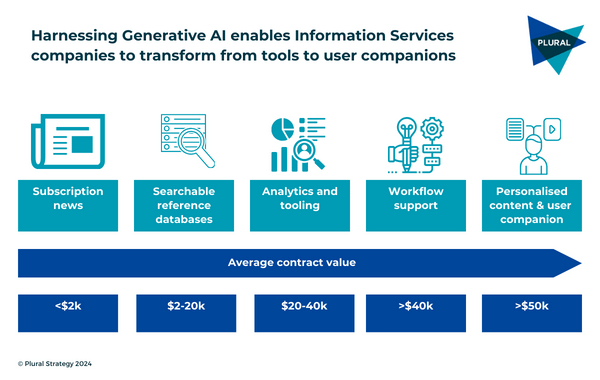
The early GenAI innovations suggest that information companies which harness AI effectively may be able to redefine the role they play for their customers. These companies are changing from traditional reference-based information tools to user companions, embedded more deeply than ever before into customer workflows and processes.
Which information companies are best placed to take advantage?
While the potential benefits of GenAI are becoming clearer, the challenge is to unpick the factors which will drive success. Providers must also be aware of the risks entailed (e.g. that GenAI will allow new entrants to harness public data sources effectively) and move quickly.
While there are many aspects to consider, the information providers best-positioned to leverage GenAI are those with:
- Unique, high quality data: Information companies with well curated datasets which drive specific client use cases will be well positioned to train high quality GenAI models. They have an advantage vs. GenAI-based entrants which will need to build their own databases, or rely on lower quality public sources, to train their models.
- Trust and Credibility: Information providers which have built deep trust and credibility in their industries are well-placed to drive adoption of GenAI within their customer base, and have a strong barrier to AI-based entrants.
- Specific use cases with lower error tolerance: Near term, the strongest opportunities to leverage AI are to help automate time-intensive customer use cases with low error tolerance (e.g. lawyer using GenAI chat to retrieve relevant case information).
- High-Performing, Agile Management Teams: An important driver of success is having innovative and agile management teams with a good grasp of GenAI and an established AI strategy.
Plural Strategy’s GenAI Framework
Our framework is specifically designed to help operators and investors evaluate the impact of generative AI in information services businesses, and has been used to assess recent deals in the sector.